Answering all the Hedging questions – What is Hedging, Why should one Hedge, Where can one Hedge, How Hedging Works and When Should one Hedge.
What is Hedging?
Hedging is a technique to protect the risk of investment in equity by opening up contrarian positions to make the position risk netral.
Hedging is used against the negative outcome of a possible event. Remember it doesn’t prevent the event from happening, but if it does happen and if you’re hedged, there isn’t any impact of the event or at least not as worst as it could have been.
So, hedging, is a technique by which you won’t make money but reduce the potential of a loss.
Why should one Hedge?
For long-term investors, when the market takes a corrective mode, there are 4 possibilities:
- Wait and do nothing about it.
- Book out of the long position and buy again later.
- Hedge the open position.
- Use the dips to increase your position in the stock.
Doing nothing about it is never a good option even for a long term investor.
There are multiple reason why investor prefer to keep holding their cash long positions instead of booking out and getting back in:
- Dividend – If company declares dividend, if you aren’t holding your long positions, you aren’t eligible for a dividend.
- Save tax – If you are making handsome gains on your investment, selling off just ahead of the news can mean you will have to pay a capital gain tax which can be avoided with a hedge.
- Save on brokerages – Buying and selling in the cash market has more brokerage than in futures and options and so you can save on the brokerages.
So once you want to keep holding your long positions and still want to be protected, you have an option to Hedge. Later we will see how one can hedge their positions.
The last option is to accumulate more good quality stocks using the short term turmoil. I always prefer this and use my investment checklist and the fundamental analysis to add more to my portfolio.
Where can one Hedge?
Heding has many forms: If you are long in particular stock in the cash market, you can hedge it with
- A short position in the futures market.
- Buy put option in the options market.
- Have an index short position using the stock’s beta with respect to the index.
- A commodity position (gold, oil, etc) or a bond position
- A different position in different stock in the cash market itself.
How Hedging Works?
1. Hedging with Futures, Options or Index
Let’s see it with an example:
Say you own shares of Sun Pharma. You are a long-term (10+ years) investor but aren’t sure about the short-term (1 year or so) issues in the Pharma sector. To protect from the fall in the stock you can either have a short position in futures or can buy a put option in the options market. More about buying a put option here.
If your stock price tumbles, your loss from the long term investment will be offset by gains in either the short position in the futures or from the put option.
Note that your cash market position should be of the multiple of the lot size in futures or options to hedge the completely.
Similarly, you can hedge against the dollar for investment in a purely export oriented company like an Infosys where as a long-term investor want to protect against the potential risk due to fluctuations in the forex rates.
Or one can take a short position in the index for a long position in the stock based on the stock beta with respect to the index.
Beta is a measure of divergence of the stock price with respect to the index or in simple terms, it is the relative performance of the stock with respect to the index.
Reuters provide more updated beta value of the stock and as of today Infosys has a beta of 0.44. So if you are long on Infy and want to hedge against the index, you should have at least 0.44 times your long position’s short on Index.
So if you are invested 10L in Infy in cash market, you should have 4.4L short on index to hedge your long position.
If you are long on high beta stock where stock has a beta of more than one, your short position on Index will be higher.
Hedging with Alternate Cash Market Postion
Diversification is also a kind of hedging though not in a true sense still I prefer to hedge with stock diversification with a focused approach to investing. I avoid trading in futures, options, commodities and in forex to the extent that I don’t have my account enabled to trade in them.
So I prefer diversification to hedge.
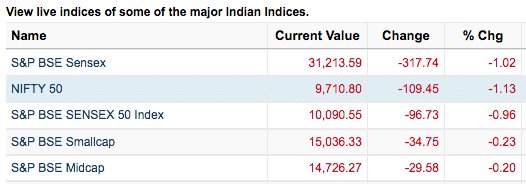
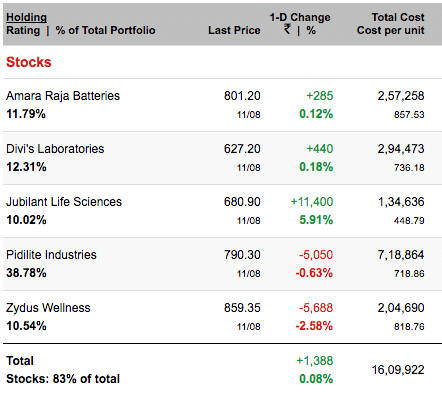
On 11th August 2017 when every major indices were down, my stock portfolio wasn’t
Chart from Moneycontrol
The portfolio saver was Jubilant Life.
I prefer focus investing over diversified investing but prefer to be holding few companies in different sectors and rarely have more than one company in the same business.
When Should one Hedge?
Hedging (unlike diversification) is mainly news driven. When you expect a news where you aren’t sure about the possible outcome, you can hedge your position.
Bad quarterly result for a company, rise in raw material prices for a company, before the union budget, before FED meets, before the RBI policies etc.
Once the volatility due to the news is discounted in the price, you can unhedge your position and let the profit rise.
Final Thoughts
There are debt funds, arbitrage funds but there aren’t any hedge funds still avaialble in India. So it isn’t very popular among Indian retail investors.



Well explained Shabbir in such a simple manner. Thanks for answering my AMA
The pleasure is all mine Rahul.